1.
Kärrholm J. Roentgen stereophotogrammetry. Review of orthopedic applications. Acta Orthop Scand. 1989;60(4):491-503. [PubMed]
2.
Valstar ER, Nelissen RGHH, Reiber JHC, Rozing PM. The use of Roentgen stereophotogrammetry to study micromotion of orthopaedic implants. I. 2002;56(5-6):376-389. doi:10.1016/s0924-2716(02)00064-3
3.
Selvik G. Roentgen stereophotogrammetry. A method for the study of the kinematics of the skeletal system. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1989;232:1-51. [PubMed]
4.
Vrooman H, Valstar E, Brand G, Admiraal D, Rozing P, Reiber J. Fast and accurate automated measurements in digitized stereophotogrammetric radiographs. J Biomech. 1998;31(5):491-498. [PubMed]
5.
Kaptein B, Valstar E, Stoel B, Rozing P, Reiber J. A new model-based RSA method validated using CAD models and models from reversed engineering. J Biomech. 2003;36(6):873-882. [PubMed]
6.
Kärrholm J, Gill R, Valstar E. The history and future of radiostereometric analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;448:10-21. [PubMed]
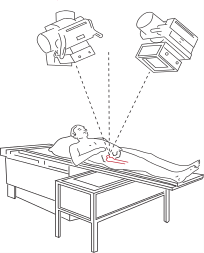 Roentgen Stereogrammetric Analysis (RSA) is a radiographic method used to measure skeletal and implant movements with very high resolution in vivo
Roentgen Stereogrammetric Analysis (RSA) is a radiographic method used to measure skeletal and implant movements with very high resolution in vivo